Picky eaters are very sensitive to feed quality. Be sure that premixed feeds and straight grains are within their printed expiration date. In addition, store feeds correctly to avoid mold or oxidation from exposure to air and moisture. In very hot weather, buy only enough feed to last a week or so. Prevent fermentation of grains and molasses in storage. Be a discerning customer when buying hay and chaff, and accept only clean, fresh-smelling forages that are free from weeds, dust, mold, and evidence of rodent infestation.
Forage:
In cases where horses are being fed a lot of grain, adding more forage to the diet can help to avoid problems such as gastric ulcers and hindgut acidity that may reduce appetite. Add forage as long-stem forage (hay or pasture) rather than chaff or other fiber sources. Offering at least 1% of body weight in forage per day is the best way to avoid digestive problems that may dull appetite.
The high glycemic index of grain feeds and the corresponding high blood sugar and insulin levels following grain meals can suppress appetite. As hard feed rations are increased, overall appetite is suppressed.
Horses find best-quality forage most palatable. The hay does not have to be prime lucerne (alfalfa) or clover hay; any clean hay that is free of dust and mold with plenty of leaf and not too much rough, woody stem that has been cured and stored correctly is preferred. Rough, stalky hay is retained in the digestive tract longer than good-quality, leafy hay. This can affect appetite and intake of forage. Although this type of hay is unsuitable for picky eaters, it can be useful for overweight animals.
In horses that must consume concentrated energy, lucerne (alfalfa) or clover are good choices but are often better in combination with non-legume hays (grass, and cereal hays) than fed alone, where they can sometimes be too rich and cause scouring and further digestive upset.
B Vitamins:
In some cases, a deficiency of B vitamins can be the reason for suppressed appetite. Feeding plenty of forage ensures correct hindgut digestion, allowing adequate production of essential B vitamins in most cases. However, in horses that are working very hard, or those that are under stress or are scouring, B-vitamin production may fall short of requirements.
Supplementing B vitamins to horses with reduced appetite can stimulate appetite. Supplementation is best in an oral form rather than injectibles. For horses that refuse feed, mix powders with water, Give orally via a dosing syringe. Supplements should contain the full complex of B group vitamins at appropriate levels.
A course of daily supplementation for 14 to 20 days will help to stimulate appetite in horses that have gone off feed suddenly. Strategic supplementation prior to and at a show and competition can help to maintain appetite at these critical times. In some rare cases, regular supplementation seems to be required, with the horse going off feed as soon as the supplement is taken away, but correct nutritional and work balance can often alleviate inappetence enough that this is not necessary.
Oil and Fat:
In horses where no cause of poor appetite can be established, the owner or manager must come up with clever ways to get enough energy into the horse to do the job that is required in a safe way that will not affect the horse’s behavior or performance. High-fat feeds and fat/oil supplements can be a great way to get extra calories into the feed bucket in a relatively small volume of feed.
Oil and fat contains about three times the amount of energy as oats on a volume to volume basis. One cup of oil has about the same energy as 1 kg (2.2 lb) of oats. Adding oil or a high-fat supplement increases the energy density of the feed, making each mouthful more calorific.
Even if the horse only eats half of the supplemented feed, the calories taken in are significantly more than with grain feed alone. Appropriate oil choices are canola, corn (the most palatable), sunflower, or mixed vegetable oil. Choose only new oil. Avoid any oil claiming to be recycled or anything from the restaurant industry. This has been used for frying and has different properties from fresh oil.
Other high-fat supplements include rice bran, sunflower seeds, and soybean meal. These can be useful for horses with an aversion to oil. It can be used in combination with oil to reduce the overall volume of oil required. A regular amount is 1 to 2 cups of oil per day or a total of 1 to 2 kg (2.2 to 4.4 lb) of high-fat supplements with or without added oil.
Electrolytes and Salt:
Electrolytes and salt are very important in horse diets. Particularly in working horses. However, feeding too much can suppress appetite and reduce feed palatability. Generally, palatability is reduced once salt is included at more than 1% of the feed. With picky eaters, the tolerance level can be much lower than that.
In many cases, it is better to allow free-choice salt separately from the feed. Dose horses daily by syringe to get the right amount of salt and electrolytes into them. When adding or increasing salt in the feed, the best approach is to do it gradually. This will not always work with picky eaters. Yet, it can help to get the horse eating if no drastic changes are noticed in the feed.
In cases where it is imperative that the horse eats. For example, such as if the horse is sick and weak. If refusal of feed over a period of time while away at competition is affecting performance. If a horse is competing in a long-distance endurance event and is not eating well along the way. The smorgasbord approach can be very useful. Providing a range of different feedstuffs in an attempt to find something that the horse will voluntarily eat will help to satisfy the immediate requirement of getting something into the horse.
New Feedstuffs:
Do not offer new and strange feedstuffs to horses. However, in cases where the horse must eat something, this rule takes a back seat. Smorgasbord meals are usually small (around 0.5 to 1 kg or 1.1 to 2.2 lb per feed type). Once the horse has chosen a particular feed, the others are generally removed. Feedstuffs offered may include a variety of hay types. The preferred type may surprise owners who imagine that prime lucerne (alfalfa) must be the only hay they should try. Do not underestimate the palatability of fresh grass.
In terms of hard feed, the menu may include pellets. In addition, sweet feeds of different types (micronized, steam-flaked, and so on), and straight grains such as steam-flaked barley or straight oats. Leave additives and supplements out of the feed. However, additions such as carrots, apples, a little molasses, apple cider vinegar, or even fruit juice can sometimes be just the temptation the horse needs. The traditional bran mash can be a powerful tool in trying to tempt the picky eater.
A good helping of wheat bran or pollard with the addition of a handful of grain and perhaps some molasses and some carrots and/or apples soaked with warm water and fed fresh and warm can be to a horse as chicken soup is to a convalescing human patient. Bran mashes are often the first feed of choice in equine veterinary hospitals following surgery. For good reason: their proven palatability and as a great way of getting some vital fluids into a horse.
Dealing with picky eaters can be frustrating. The trick is to work out why the horse is not eating. Then, fix the root cause of the problem.
Resources:
In conclusion, do you have questions about Strategies for Increasing Appetite and Tempting Picky Eaters? Contact us at J & J Hay Farms by clicking here!
Article by KER.
 The following guide will help you to get your horse to drink more water during winter. Water is the most essential aspect of any horse’s diet. Without adequate water intake, horses will not survive.
The following guide will help you to get your horse to drink more water during winter. Water is the most essential aspect of any horse’s diet. Without adequate water intake, horses will not survive.
 With winter approaching, horse owners will be looking for a source of hay to feed
With winter approaching, horse owners will be looking for a source of hay to feed  Winter seems so far away, but it is just around the corner. Are you ready? Is your horse ready? Learn how to feed horses in the winter in this post.
Winter seems so far away, but it is just around the corner. Are you ready? Is your horse ready? Learn how to feed horses in the winter in this post.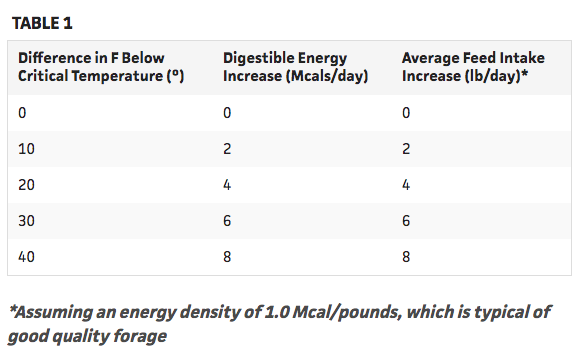
 Give Colic the Cold Shoulder This Winter: Colic can strike at any time of the day, month, or year. However, impaction colic occurs more frequently in winter. Decreased water intake usually carries the blame for these impactions. Impactions are a blockage in the large colon. Any feedstuff undergoing digestion causes it. Other management factors also contribute to the problem.
Give Colic the Cold Shoulder This Winter: Colic can strike at any time of the day, month, or year. However, impaction colic occurs more frequently in winter. Decreased water intake usually carries the blame for these impactions. Impactions are a blockage in the large colon. Any feedstuff undergoing digestion causes it. Other management factors also contribute to the problem. Strategies for Increasing Appetite and Tempting Picky Eaters: Many factors and situations may reduce a horse’s appetite. It’s important to find and correct whatever it is—illness, pain, discomfort, environment—that keeps a horse from diving eagerly into his feed. As the situation is being corrected, owners can try some of the following strategies to encourage a more healthy appetite.
Strategies for Increasing Appetite and Tempting Picky Eaters: Many factors and situations may reduce a horse’s appetite. It’s important to find and correct whatever it is—illness, pain, discomfort, environment—that keeps a horse from diving eagerly into his feed. As the situation is being corrected, owners can try some of the following strategies to encourage a more healthy appetite. Advantages of Haynets and Hay Feeders for Horses: While forage is the most important part of a horse’s diet, circumstances arise when intake should be limited. Obese horses and ponies with metabolic conditions, for example, may need to have calorie intake controlled carefully to avoid overconsumption of energy. Limiting forage intake can mean less time spent chewing, and with this comes a reduction in saliva production and stomach-acid buffering, all of which sets the stage for gastric ulcers and possible colic.
Advantages of Haynets and Hay Feeders for Horses: While forage is the most important part of a horse’s diet, circumstances arise when intake should be limited. Obese horses and ponies with metabolic conditions, for example, may need to have calorie intake controlled carefully to avoid overconsumption of energy. Limiting forage intake can mean less time spent chewing, and with this comes a reduction in saliva production and stomach-acid buffering, all of which sets the stage for gastric ulcers and possible colic. Feeding and Caring for Horses During Cold Weather: Healthy horses usually get along fine in moderately cold weather. A little more care may be necessary for very young or very old equines. In addition, those that are ill or have any sort of chronic health challenge. In extremely cold, wet, or windy weather, almost all horses will benefit from a few adjustments to management.
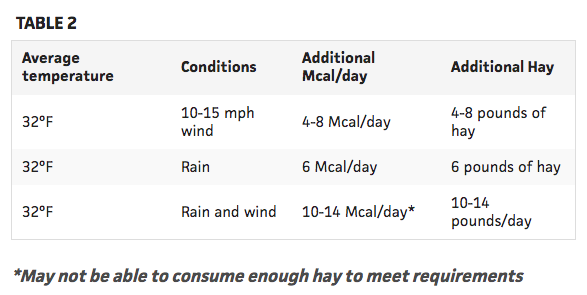
Feeding and Caring for Horses During Cold Weather: Healthy horses usually get along fine in moderately cold weather. A little more care may be necessary for very young or very old equines. In addition, those that are ill or have any sort of chronic health challenge. In extremely cold, wet, or windy weather, almost all horses will benefit from a few adjustments to management. As the warm summer months draw to a close, horse owners stock up on hay for the winter. The hay man has a variety of hays available, including the yellow or brown, less leafy fall hays. Although they might not be as physically attractive and green as the hay harvested earlier in the summer, there are many benefits to late-season hay for horses.
As the warm summer months draw to a close, horse owners stock up on hay for the winter. The hay man has a variety of hays available, including the yellow or brown, less leafy fall hays. Although they might not be as physically attractive and green as the hay harvested earlier in the summer, there are many benefits to late-season hay for horses. Fall Maintenance for Healthy Winter Horses:
Fall Maintenance for Healthy Winter Horses: Your Horse: Avoid Being Felled by Fall Founder: If you’ve been involved with horses for any length of time, you’re no stranger to the anguish caused by laminitis. You may be aware of common causes of founder. For example: grain overload, endocrine disturbances, and overloading of supporting limbs, there’s one you may overlook: fall grazing.
Your Horse: Avoid Being Felled by Fall Founder: If you’ve been involved with horses for any length of time, you’re no stranger to the anguish caused by laminitis. You may be aware of common causes of founder. For example: grain overload, endocrine disturbances, and overloading of supporting limbs, there’s one you may overlook: fall grazing.